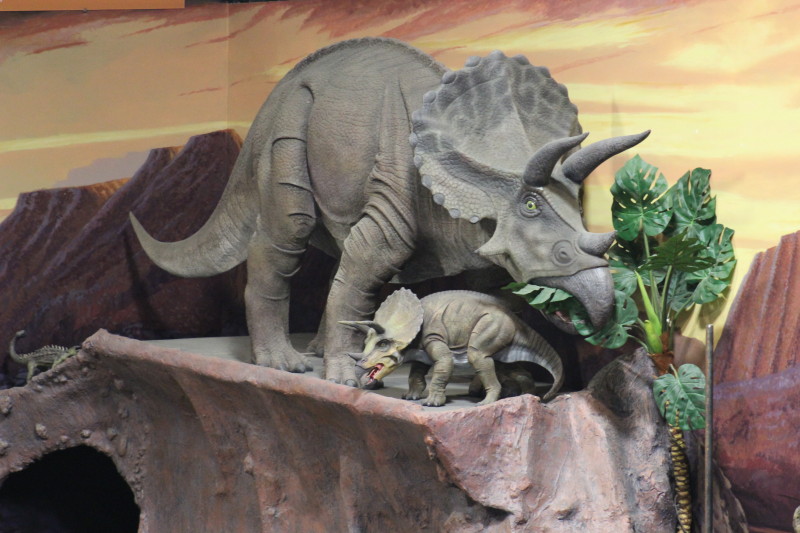
The large specimens are complete fossil animals. The lava and flat round sand stone were found on site.
The large stones have footprints and tail drags.
The Permian Period saw the diversification of egg laying tetrapods (four-legged land creatures). The
rainforests of the Carboniferous had disappeared and left behind vast arid deserts. Reptiles that could better cope with this environment replaced the amphibians as the dominant creature on the earth. Some of the first fourlegged land living vertebrates roamed at this time. The Edaphosaur was a Herbivore that had a sail on its back much like the Dimetrodon. The Dimetrodon was a carnivore and was one of the top predators during this time. The sail was like a radiator and allowed the cold blooded reptile to warm up earlier each morning. At the end of the Permian the largest mass extinction in earth’s history occurred killing the majority of life on earth. It took millions of years for life to recover.
The Trimerorhachis lived in the early Permian period. It was an aquatic predator that fed on fish and other small vertebrates. Their fossils are generally found in the north central area of Texas.
This is a replica of a fossil Mesosaurus that lived in the early Permian period. Mesosaurs were fully aquatic reptile predators that had fairly large teeth. Its nostrils were placed on the top of its snout so that only the top of the head had to surface for air. This is similar to modern day crocodiles.
The Microsaur lived in the early Permian and were small amphibians. These are the limb bones of a Microsaur and you can see that these were very small creatures. They are the possible ancestors of the
Salamanders. Next to the limb bones are Amphibian teeth. At this time amphibians could get fairly large and had sharp teeth that they used to catch their prey.
A piece of petrified wood from Brazil tells scientists the type of trees that grew during the Permian
period. As you can see the tree is not very large. The climate at this time was fairly dry and desert like. Therefore plant life was small and large forests were not as common. Found along with the Dimetrodon in the Diarama were two corprolites. This is dinosaur “poop” and is sometimes found near dinosaur remains.